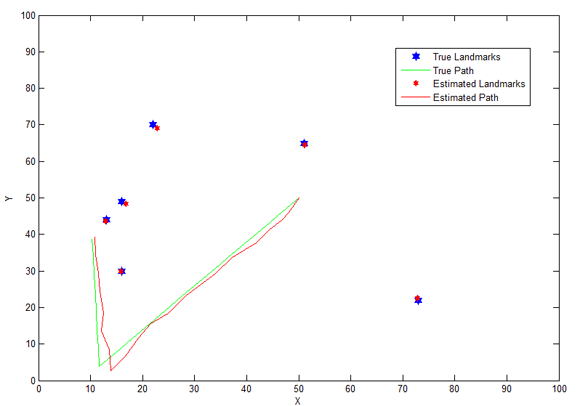
Datei: myGraphSLAM.m
function [] = myGraphSLAM(N, numLandmarks, worldSize, measurementRange, motionNoise, measurementNoise, distance, plotWorld) if exist('plotWorld', 'var') == 0 || isempty(plotWorld) plotWorld = boolean(0); % false end %% Configuration % %numLandmarks = 9; % number of landmarks %N = 10; % time steps %worldSize = 100.0; % size of world %measurementRange = 50.0; % range at which we can sense landmarks %motionNoise = 2.0; % noise in robot motion %measurementNoise = 2.0; % noise in the measurements %distance = 20.0; % distance by which robot (intends to) move each iteratation if plotWorld figure(); end data=makeData(N, numLandmarks, worldSize, measurementRange, motionNoise, measurementNoise, distance, plotWorld); [ result, Omega, Xi ] = slam(data, N, numLandmarks, worldSize, motionNoise, measurementNoise); printResult(N, numLandmarks, result); if plotWorld for i = 0:N-1 estimatedPose(i+1,:) = [result( (2*i)+1 ), result( (2*i+1)+1 )]; end for i = 0:numLandmarks-1 estimatedLandmark(i+1,:) = [result( (2*(N+i))+1 ), result( (2*(N+i)+1)+1 )]; end hold on; plot(estimatedLandmark(:,1),estimatedLandmark(:,2), 'rh', 'MarkerSize', 7, 'MarkerFaceColor', 'r' , 'MarkerEdgeColor', 'r'); %path = [worldSize / 2.0, worldSize / 2.0]; plot(estimatedPose(:,1), estimatedPose(:,2), 'r-'); axis([0 worldSize 0 worldSize]); hold off; legend('True Landmarks', 'True Path', 'Estimated Landmarks', 'Estimated Path'); end end %%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%% %% Robot Class Functions from CS373 - Course from UDACITY %% %%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%% %% %% %%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%% %% %% this is the robot class %% %% our robot lives in x-y space, and its motion is %% pointed in a random direction. It moves on a straight line %% until is comes close to a wall at which point it turns %% away from the wall and continues to move. %% %% For measurements, it simply senses the x- and y-distance %% to landmarks. This is different from range and bearing as %% commonly studies in the literature, but this makes it much %% easier to implement the essentials of SLAM without %% cluttered math %% %%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%% % init: % creates robot and initializes location to 0, 0 % function [ robot ] = createRobot(worldSize, measurementRange, motionNoise, measurementNoise) if isempty(worldSize) worldSize = 100.0; end if isempty(measurementRange) measurementRange = 30.0; end if isempty(motionNoise) motionNoise = 1.0; end if isempty(measurementNoise) measurementNoise = 1.0; end robot = []; robot.measurementNoise = 0.0; robot.worldSize = worldSize; robot.measurementRange = measurementRange; robot.x = worldSize / 2.0; robot.y = worldSize / 2.0; robot.motionNoise = motionNoise; robot.measurementNoise = measurementNoise; robot.landmarks = []; robot.numLandmarks = 0; end % make random landmarks located in the world % function [ robot ] = makeLandmarks(robot, numLandmarks) robot.landmarks = []; for i = 1:numLandmarks robot.landmarks(i,:) = [randi([1 robot.worldSize]), randi([1 robot.worldSize])]; end robot.numLandmarks = numLandmarks; end % move: attempts to move robot by dx, dy. If outside world % boundary, then the move does nothing and instead returns failure % function [ robot, success ] = robotMove(robot, dx, dy) newX = robot.x + dx + (-1 + 2.0 * rand(1)) * robot.motionNoise; newY = robot.y + dy + (-1 + 2.0 * rand(1)) * robot.motionNoise; if newX <= 0 || newX > robot.worldSize || newY <= 0 || newY > robot.worldSize success = boolean(0); % return false else robot.x = newX; robot.y = newY; success = boolean(1); % return true end end % sense: returns x- and y- distances to landmarks within visibility range % because not all landmarks may be in this range, the list of measurements % is of variable length. Set measurement_range to -1 if you want all % landmarks to be visible at all times % function [ Z ] = robotSense(robot) Z = []; for i = 1:robot.numLandmarks dx = robot.landmarks(i,1) - robot.x + (-1 + 2.0 * rand(1)) * robot.measurementNoise; dy = robot.landmarks(i,2) - robot.y + (-1 + 2.0 * rand(1)) * robot.measurementNoise; if robot.measurementRange < 0 || abs(dx) + abs(dy) <= robot.measurementRange Z = [Z; i, dx, dy]; end end end % print robot location % function [] = robotDisplay(robot) % display current position disp(sprintf('Robot: [x=%.5f y=%.5f]', robot.x, robot.y)); end % this routine makes the robot data % function [ data ] = makeData(N, numLandmarks, worldSize, measurementRange, motionNoise, measurementNoise, distance, plotWorld) complete = boolean(0); % false while complete == 0 data = []; % make robot and landmarks r = createRobot(worldSize, measurementRange, motionNoise, measurementNoise); r = makeLandmarks(r, numLandmarks); seen = boolean( zeros( numLandmarks, 1 ) ); % guess an initial motion orientation = rand(1) * 2.0 * pi; dx = cos(orientation) * distance; dy = sin(orientation) * distance; for k = 1:(N-1) % sense Z = robotSense(r); % check off all landmarks that were observed for i = 1:size(Z,1) seen(Z(i,1)) = boolean(1); % true end % move [ r, success ] = robotMove(r, dx, dy); while success == 0 % if we'd be leaving the robot world, pick instead a new direction orientation = rand(1) * 2.0 * pi; dx = cos(orientation) * distance; dy = sin(orientation) * distance; [ r, success ] = robotMove(r, dx, dy); end % memorize data append(1,1).Z = Z; append(1,1).motion = [dx,dy]; data = [data; append]; end % we are done when all landmarks were observed; otherwise re-run if sum(seen) == numLandmarks complete = boolean(1); if plotWorld xlabel('X'); ylabel('Y'); plot(r.landmarks(:,1), r.landmarks(:,2), 'bh', 'MarkerSize', 10, 'MarkerFaceColor', 'b', 'MarkerEdgeColor', 'b'); hold on; path = [worldSize / 2.0, worldSize / 2.0]; for i = 1:size(data,1) path(i+1,:) = [path(i,:) + data(i).motion]; end plot(path(:,1), path(:,2), 'g-'); axis([0 worldSize 0 worldSize]); hold off; end else complete = boolean(0); end end disp(' '); for i = 1:size(r.landmarks,1) disp(sprintf('Landmarks: [x=%.5f y=%.5f]', r.landmarks(i,1), r.landmarks(i,2))); end %print ' ' %print 'Landmarks: ', r.landmarks %print r end % full_slam - retains entire path and all landmarks % Feel free to use this for comparison. % function [ mu, Omega, Xi ] = slam(data, N, numLandmarks, worldSize, motionNoise, measurementNoise) % Set the dimension of the filter dim = 2 * (N + numLandmarks); % make the constraint information matrix and vector Omega = zeros(dim, dim); Omega(1,1) = 1.0; Omega(2,2) = 1.0; Xi = zeros(dim, 1); Xi(1,1) = worldSize / 2.0; Xi(2,1) = worldSize / 2.0; % process the data for k = 0:size(data,1)-1 % n is the index of the robot pose in the matrix/vector n = k * 2; % measurement = []; motion = []; measurement = data(k+1).Z; motion = data(k+1).motion; % integrate the measurements for i = 0:size(measurement,1)-1 % m is the index of the landmark coordinate in the matrix/vector m = 2 * (N + measurement(i+1,1)-1); % update the information maxtrix/vector based on the measurement for b = 0:1 Omega(n+b+1,n+b+1) = Omega(n+b+1,n+b+1) + 1.0 / measurementNoise; Omega(m+b+1,m+b+1) = Omega(m+b+1,m+b+1) + 1.0 / measurementNoise; Omega(n+b+1,m+b+1) = Omega(n+b+1,m+b+1) - 1.0 / measurementNoise; Omega(m+b+1,n+b+1) = Omega(m+b+1,n+b+1) - 1.0 / measurementNoise; Xi(n+b+1,1) = Xi(n+b+1,1) - measurement(i+1,2+b) / measurementNoise; Xi(m+b+1,1) = Xi(m+b+1,1) + measurement(i+1,2+b) / measurementNoise; end end % update the information maxtrix/vector based on the robot motion for b = 0:3 Omega(n+b+1,n+b+1) = Omega(n+b+1,n+b+1) + 1.0 / motionNoise; end for b = 0:1 Omega(n+b+1 ,n+b+2+1) = Omega(n+b+1 ,n+b+2+1) - 1.0 / motionNoise; Omega(n+b+2+1 ,n+b+1) = Omega(n+b+2+1 ,n+b+1) - 1.0 / motionNoise; Xi(n+b+1,1) = Xi(n+b+1,1) - motion(b+1) / motionNoise; Xi(n+b+2+1,1) = Xi(n+b+2+1,1) + motion(b+1) / motionNoise; end end % compute best estimate mu = inv( Omega ) * Xi; end % print the result of SLAM, the robot pose(s) and the landmarks % function [ ] = printResult(N, numLandmarks, result) disp(' '); disp('Estimated Pose(s):'); for i = 0:N-1 disp( sprintf(' [%.3f, %.3f]', result( (2*i)+1 ), result( (2*i+1)+1 ) ) ); end disp(' '); disp('Estimated Landmarks:'); for i = 0:numLandmarks-1 disp( sprintf(' [%.3f, %.3f]', result( (2*(N+i))+1 ), result( (2*(N+i)+1)+1 ) ) ); end end
Full GraphSLAM-Algorithmus mit festen Markern von UDACITY-Kurs CS373
Übersetzung von python nach MatLab, Lösung des SLAM-Problems mit GraphSLAM-Algorithmus
- Full GraphSLAM
- Verwendung von festen Orientierungspunkten (Landmarks)
- Übersetzung von python nach MatLab
- Ergänzung um Visualisierung
- Aufruf z.B.: myGraphSLAM(20, 6, 100, 50, 2.0, 2.0, 5, 1)

